
Depending on the process, you may also cross out one of the following variables: T, V, P. (R is equal to the Avogadro's constant multiplied by the Boltzmann constant)Īlways remember that the nR part of any of these equations is constant – it means it may be crossed out when you transform the formula. R – The ideal gas constant = 8.314 J/(mol With just a few transformations, we can use this formula to determine all the properties of a given gas in three types of processes: isobaric, isochoric, and isothermal.īelow you will find all of the most essential, ready-to-go equations used in all those calculations, along with a quick explanation. That's why we use the combined gas law calculator (a.k.a. There are plenty of chemistry-based queries that can be solved by some form of the original ideal gas law. The molar mass of gas is not the only thing we can calculate with the ideal gas law!
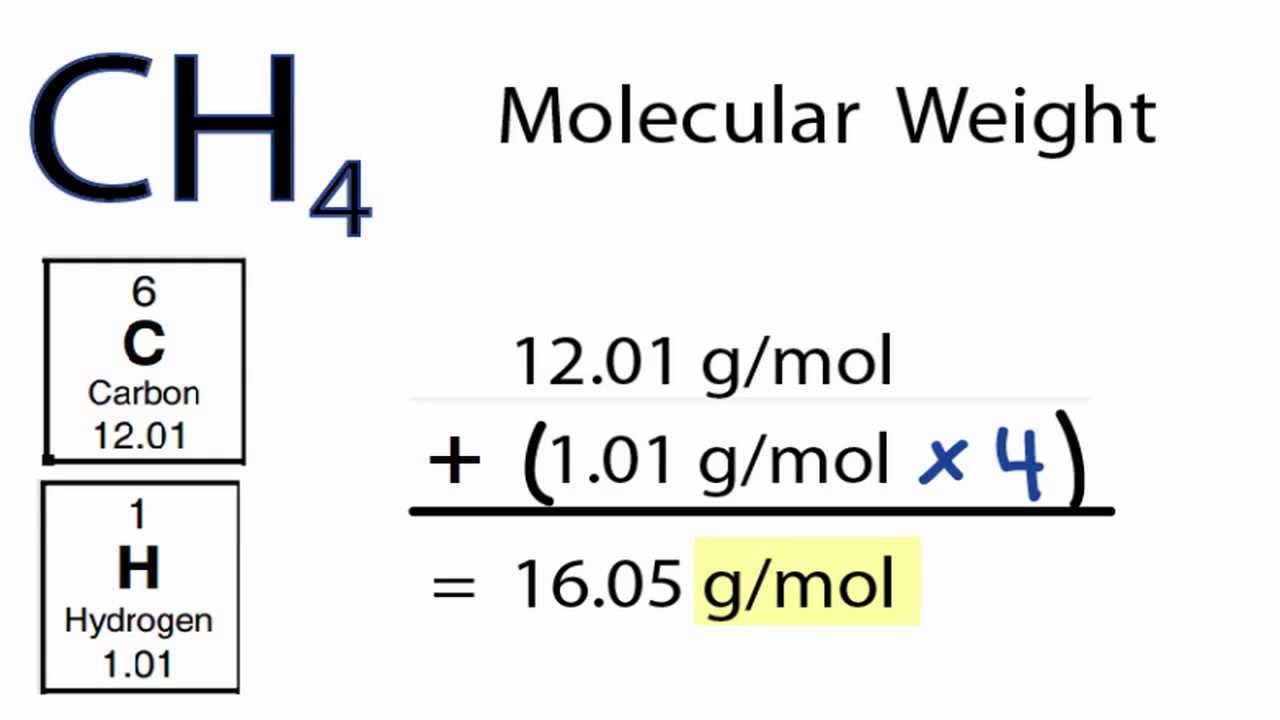
A Dalton is a unit of atomic mass equal to the mass of 1/12 of a particle of carbon ¹☬. The calculated value is numerically identical to 1 u (or 1 Da = Dalton, used in biochemistry).
Molar mass of oxygen gas how to#
It's as simple as that! Recommended units:īut your mass isn't given in grams? Don't worry why don't you take some time to discover how to properly convert between different densities and weights? If you want to work it out yourself, without the molar mass of gas calculator, be careful with the units! This particular equation uses a constant of 0.0821, which is intended for the following units: Moles = (Pressure × Volume) / (0.0821 × Temperature) Our gas law calculator uses the following equations:

Mass (not required for number of moles calculations).Volume of the gas (ml, L, dm³, m³) and.Pressure (most commonly used units: atm, kPa).You need the following data about the gas:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
